Research
Aims
Overarching Aims
- Systematically address and revisit the issue of “reduced penetrance” using hereditary movement disorders as an example
- Discover mechanisms explaining reduced penetrance in a multimodal fashion
- Develop bioinformatics and statistical tools, new ethics standards, and a sustainable Knowledge Base for the members of the Research Unit and the scientific community
- Advancement of ethics methodology for enrolling clinically unaffected mutation carriers in studies aimed at understanding reduced penetrance
Long-Term Scientific Aims
- Employ additional ‘omics’ approaches and (animal) models to validate findings
- Identify and functionally characterize non-coding variants relevant for reduced penetrance or for delaying disease expression
- Focus on epigenetic mechanisms as a likely additional important modifier of penetrance
- Build on newly identified modifiers of reduced penetrance to gain mechanistic insight through functional studies
- Extend and further deepen phenotyping by including neuroimaging and electrophysiology techniques (endophenotyping), as well as data on environmental factors
- Translate findings into genetic counseling routines
- Explore newly identified genomic factors relevant for the reduction in penetrance as potential therapeutic targets
Projects
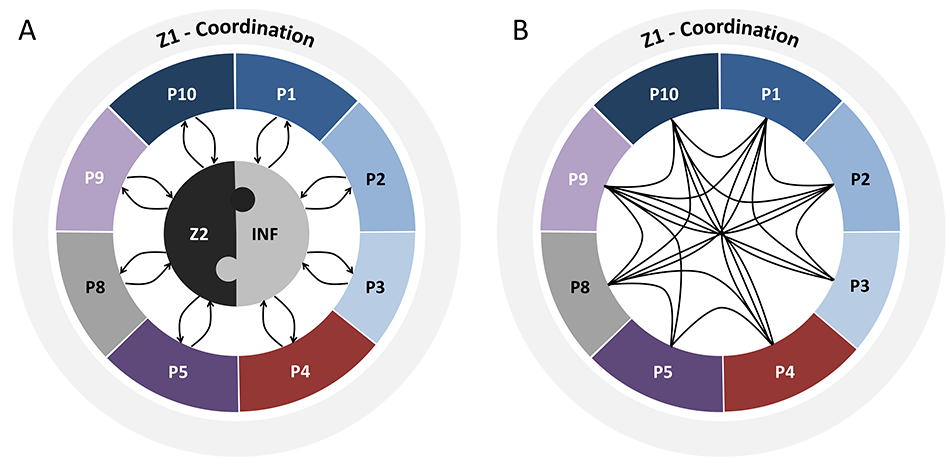
The figure below shows the interaction between the projects of the Research Unit. Projects P1-P8 all address different aspects of reduced penetrance in movement disorders with a focus on Parkinson’s disease (blue), monogenic dystonia (red), dystonia-parkinsonism (purple), dystonia in general (pink), or method development/analysis (gray). (A) Data from all projects are continuously provided by, and fed back to, the Central Cohort Project (Z2) and to the Central Knowledge Base (INF). Likewise, data from INF (both from the literature and own preliminary or newly generated) will inform additional queries to Z2; conversely, all available and newly collected data will further complement INF with similar feedback mechanisms to and from P1-P8. Z1 serves as central coordination project of the entire Research Unit. (B) In addition, there will be direct interactions between projects P1-P8.
Molecular mechanisms defining penetrance of LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease
Mutations in the Parkinson’s disease (PD) gene Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are dominantly inherited with reduced penetrance. To date, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that trigger the onset of LRRK2-PD. To allow for better monitoring of progression and, ultimately, for the identification of penetrance-associated cellular pathways, in ProtectMove I, we investigated markers of LRRK2-PD manifestation. In fibroblasts from manifesting (LRRK2+/PD+; n=10) and non-manifesting carriers (LRRK2+/PD-; n=21) of the G2019S mutation, first, we confirmed a link between PD onset and LRRK2 phosphorylation. Second, inspired by a report connecting LRRK2 kinase activity with mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) lesions, we assessed mtDNA integrity and mitochondrial function in LRRK2+/PD- and LRRK2+/PD+ fibroblasts and observed an accumulation of mtDNA deletions and decreased complex I activity in the latter. In light of a study showing reduced urate in LRRK2+/PD+ individuals, we explored urate-induced Nrf2-ARE antioxidant signaling. Interestingly, the Nrf2-ARE target TFAM, which acts as mtDNA transcription and packaging factor was reduced in LRRK2+/PD+ neurons, increasing mtDNA exposure to reactive oxygen species. We hypothesize that a vicious cycle between environment, mitochondrial function and LRRK2 kinase activity, where the mtDNA acts as central interface, defines LRRK2-PD penetrance. To assess environmental factors contributing to penetrance and to identify relevant toxins (Objective 1), we will collect environmental exposure, diet and medication information from the LIPAD cohort (LRRK2+/PD+, n=1,500; LRRK2+/PD-, n=500; controls, n=500). Moreover, in selected persons, we will perform untargeted toxicology. To investigate penetrance-associated (epi-)genetic mtDNA alterations (Objective 2), we will perform sequencing and quantitative mtDNA analyses in blood samples from LIPAD. To determine the contribution of rare variants in nuclear genes involved in antioxidant signaling and mitochondrial function to penetrance (Objective 3), whole genome sequencing and polygenic risk score analyses will be applied to individuals from LIPAD. Finally, to test the causal link between toxin exposure, mtDNA disintegration, mitochondrial dysfunction, LRRK2 kinase activity, and antioxidant signaling (Objective 4), we will conduct RNA-Seq and functional studies in LRRK2+/PD+ and LRRK2+/PD- neurons before and after exposure to oxidative stressors, kinase inhibitors and antioxidants. The results from our study will help to guide personalized medicine approaches, which aim at delaying the onset of LRRK2-PD. Project P1 is led by Principal Investigators well-versed in epidemiological, clinical, genetic and cellular studies. Furthermore, they benefit from (inter-)national collaborations allowing to expand P1 to epigenetic and toxicology analyses. P1 is embedded in a close network of interactions within ProtectMove II. This includes projects P2-P4, P8-P10, INF, Z2 and all Cores.
Reduced penetrance in Parkin and PINK1 deficiency: Inflammation as a Parkinson’s disease penetrance modifier
Genes causative for recessively inherited Parkinson’s disease (PD) include Parkin and Phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1); rare biallelic mutations in these genes result in definite disease manifestation. On the other hand, heterozygous mutations – occurring in about 2% of the population – may predispose to PD in a dominant manner with highly reduced penetrance. PD is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta, and there is new evidence that mitochondrial dysfunction-induced inflammation plays a role in the pathogenesis of Parkin- and PINK1-linked PD: We recently found that patients with heterozygous mutations have a higher heteroplasmic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) variant load compared to healthy mutation carriers suggesting that penetrance of Parkin and PINK1 mutations are influenced by low-level mtDNA heteroplasmy. Moreover, we explored the role of inflammation in PINK1- or Parkin-associated PD and detected elevated interleukin 6 levels in Parkin mutation carriers compared to healthy controls. The overarching goal of Project P2 is to define cytokine signatures and to further explore inflammatory pathways in patients with Parkin and PINK1 deficiency. We will determine the levels of inflammatory factors in serum and cerebrospinal fluid samples by performing a cytokine panel analysis from affected vs. unaffected Parkin and PINK1 mutation carriers (Objective 1). Further, we will study microglia activation in Parkin and PINK1 deficiency models by assessing multiple extracellular cytokine analytes and live-cell imaging of microglia under basal conditions and in response to mitochondrial and inflammatory stressors in an iPSC-derived neuron/microglia co-culture (Objective 2). To pinpoint the pathways and factors involved in the protective role of Parkin and PINK1 in neuroinflammation and to explore pathways that may explain the absence of clinical parkinsonism in unaffected heterozygous mutation carriers, we will perform transcriptome profiling of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neuron/microglia co-cultures by single-cell sequencing. These pathways will then be further validated in pharmacological rescue experiments by treating the cultures with specific agonists and antagonists of selected pathways (Objective 3). We will utilize state-of-the-art technologies, i.e., iPSCs and single-cell RNA sequencing. The project builds on the extensive expertise of the PIs in genetics of movement disorders and the generation and use of neuronal models from iPSCs.
Modifiers of Parkin and PINK1 mutation penetrance in Parkinson’s disease: Endogenous human models
Mutations in PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and the E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin lead to recessive forms of Parkinson’s disease (PD). It has been shown that PINK1 and Parkin work together in a common pathway maintaining mitochondrial function and control removal of damaged mitochondria through mitophagy. Interestingly, heterozygous mutations in PINK1 and Parkin increase the risk to develop PD and may even be viewed to act in a dominant fashion with highly reduced penetrance. This suggests the existence of differentially expressed protective genes or pathways between affected and unaffected mutation carriers. Since PD is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta, it is imperative to investigate potential genetic modifiers influencing the penetrance of heterozygous Parkin and PINK1 mutations in these neurons in a cell-type specific manner. The induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology has opened up a novel avenue to generate PD patient- (and healthy control)-derived dopaminergic neuronal cultures. Several protocols have been developed to generate iPSC-derived tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive dopaminergic neuronal cultures, however, they all contain only a small proportion of TH-positive neurons. In addition, there is substantial variability in the percentage of TH-positive neurons between differentiations and even between samples within the same differentiation. These differences occur independently of the mutational status. To overcome this limitation, we established an efficient method to generate human iPSC TH-mCherry reporter lines using CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing. Upon differentiation into heterogeneous dopaminergic neuronal cultures, only mCherry-positive (TH-positive) cells will be isolated from the rest of the culture using fluorescence- activated cell sorting to obtain homogenous, TH-positive population of neurons (Objective 1). Next, we aim to identify genetic modifiers influencing the penetrance of heterozygous Parkin and PINK1 mutations employing a multi-omic transcriptome and proteome expression analysis on pure iPSC- derived dopaminergic cultures obtained from affected and unaffected heterozygous mutation carriers followed by an integrated computational network analysis (Objective 2). Finally, we aim to validate modifiers identified in Objective 2 and elucidate their mechanistic role using well-established PD cellular phenotypes such as mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and dopamine metabolism as readouts (Objective 3). We will provide cutting-edge technologies, i.e., CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing (Objective 4) to several other projects of the Research Unit. Data generated in this project will be extensively exchanged with other projects focusing on PINK1- and Parkin-associated PD within the ProtectMove consortium. Methodological aspects of the multi-omics analysis will be discussed within Z2 and with P4.
Modifiers of penetrance and expressivity in monogenic dystonia: Insights from systems biology
Mutations in several genes, including THAP1 (THAP domain-containing apoptosis-associated protein 1), SGCE (sarcoglycan, epsilon), and GCH1 (GTP cyclohydrolase 1) have been confirmed as inherited cause of dystonia. Penetrance of mutations in these genes is about 50%, and there is enormous variable expressivity among the affected carriers. In the first funding period, we focused on genetic modifiers of THAP1 penetrance. For this, we generated 20 iPSC clones from fibroblast lines of 5 affected and 5 unaffected THAP1 mutation carriers. These clones and 14 matched control lines have been differentiated into cortical neuronal lines and used for transcriptome analysis. Further, 13 affected and unaffected THAP1 mutation carriers were whole genome-sequenced and Chromosome Conformation Capture-on-Chip (4C) data of a cortical neuronal line without THAP1 mutation were generated. Using these comprehensive data resources, we demonstrated differential expression of several genes linked to diverse pathways including response to type I interferon, membrane fusion, and mitochondrial fission. For several of those genes, binding of the THAP1 transcription factor has been shown within the respective promoter regions (ENCODE data). Further, the genome data ruled out simple, coding sequence variants in other dystonia genes in the affected carriers. Finally, a common variant within the promoter of KAT6A (lysine acetyltransferase 6A) has been nominated as a potential modifier of THAP1 penetrance based on 3D interaction with the THAP1 gene and segregation in a family.
Within this proposal, the overall hypothesis is that penetrance and expressivity of mutations in THAP1, SGCE, or GCH1 are modified by further genetic variants and/or epigenetic marks affecting gene expression and/or metabolites. To substantiate this hypothesis, we will re-analyze existing data for THAP1 with a focus on molecular function combining transcriptome, genome, and regulome data in a trans-Omics multi-variate modeling approach to elucidate synergistic actions relevant to the penetrance of THAP1 mutations (Objective 1). We will broaden our focus to SGCE and GCH1. While the reduced penetrance in SGCE is mainly explained by maternal imprinting, as we demonstrated earlier, the impact of differential methylation and gene expression on the variable expressivity is largely elusive and will be targeted by transcriptome, genome, and methylome studies (Objective 2). Finally, the highly reduced penetrance in, especially, male GCH1 mutation carriers will be investigated by transcriptomics, genome sequencing, and metabolomics (Objective 3). This approach will contribute to a better understanding of molecular variations in THAP1, SGCE, and GCH1 mutation carriers and potentially elucidate factors influencing reduced penetrance and variable expressivity of mutations in these genes.
P4 will closly collaborate with P5, P8, and P9 in terms of dystonia, and methodologically with P10 and the Cores in Z2, P1 and P3.
Mechanisms of penetrance and expressivity in X-linked dystonia- parkinsonism
X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (XDP, DYT-TAF1) is a severe neurodegenerative disorder caused in all patients by a founder pathogenic variant on the X chromosome, i.e., a ~2,6-kb SINE-VNTR- Alu retrotransposon (SVAR) insertion in intron 32 of TAF1 (gene encoding TBP-associated factor 1). Despite this seemingly identical genetic cause and environmental and genetic isolation (all patients are Filipino and the majority of them live on an island in the Philippines), the affected individuals display wide variability in the severity and type of signs/symptoms as well as in age and site of disease onset. Therefore, the hypothesis of our initial application (P5 project – first funding period) was that the phenotypic variability seen in XDP is modified by the action of genetic factors influencing disease expression, and our overarching goal was to identify those factors. Indeed, using a genome- wide association study (GWAS) approach, in the initial three years of our project, we discovered three such candidate modifiers that likely act by regulating expression levels of the MSH3 and PMS2 genes. Additional functional characterization and the exact mode of action of the genetic factors identified in the initial P5 will be further investigated in the P9 of the second funding period together with the penetrance modifiers uncovered by other GWASs performed in the first funding period.
In addition, using a hypothesis-driven approach, we have shown that the length of a polymorphic (CCCTCT)n repeat within the XDP-causing SVAR insertion seems to inversely correlate with age at onset and severity of symptoms of XDP in patients. This finding placed XDP among other neurological repeat-expansion disorders and contrived a plethora of plausible scenarios and questions regarding the mechanism of action of this hexanucleotide repeat. Therefore, we postulate that several repeat-expansion-related pathogenic mechanisms, TAF1 expression dysregulation, or other factors, acting upstream from the hexanucleotide repeats may contribute to the phenotypic variability in XDP. To address our hypothesis, we will investigate i) the role of RNA foci and repeat- associated non-ATG (RAN) translation peptides (toxic species featured in numerous repeat- expansion diseases) (Objective 1) and ii) SVAR insertion-mediated alteration of TAF1 expression (through changes in transcription-relevant regulatory elements, protein binding, or epigenetic status) (Objective 2) in neuronal overexpression and patient-derived endogenous cellular XDP models. Importantly, although this project seemingly targets a specific movement disorder occurring in a specific (and relatively small worldwide) patient population, it has a far larger global significance given that it investigates mechanisms that are fundamental for the pathogenesis, disease modification, and potential therapeutic treatment of numerous other neurological (repeat-expansion) conditions.
Mendelian randomization and polygenic risk scores to understand reduced penetrance in movement disorders
Over the past decades, high-throughput technologies such as next-generation DNA sequencing and genome-wide association (GWA) together with large international consortia have produced an ever- increasing number of phenotype-associated genetic variants have been found for various common complex diseases in humans. To exploit this deluge of data reasonably, stringent dimensionality reduction is required. In this project, we will focus on ways to achieve such enhancement by two state-of-the-art analytical methods, namely Mendelian randomization (MR) and the use of Polygenic Risk Scores (PRS) with the aim to explain the reduced penetrance of known movement disorder mutations.
MR is a well-established technique for exploring causality between modifiable risk factors and disease outcome, using genetic variants as instrumental variables with the potential to overcome the problem of confounding and reverse causality. It has become more and more popular over the past years especially given the huge amount of data publicly available from GWA studies. In the first funding period of ProtectMove, we have already shown the promise of this technique for the use in movement disorders, exploring causal factors that facilitate the understanding of penetrance of Parkinson’s Disease (PD). In the second funding period, we will pursue to investigate causal hypotheses for PD, including also PD age of onset, and dystonia with a focus on classical risk factors and inflammation markers (Objective 1), as well as omics markers (Objective 2).
PRS allow summarizing the polygenic risk component of a disease in a single numerical value. In part 2 of P8, we will differentiate between PD in mutation carriers (PINK1 (gene encoding phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1), Parkin, LRRK2 (gene encoding Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2); ‘monogenic PD’) and the more common ‘idiopathic PD’. We will first use simulations to ascertain, under different levels of etiological overlap, how much of the disease risk in monogenic PD can be explained by a PRS for idiopathic PD (Objective 3). After developing new most predictive PRS for both idiopathic and monogenic PD, we will estimate the potential of these scores for modelling the penetrance and variable expressivity of known PD mutations for monogenic PD (Objective 4). Thus, part 2 of P8 will serve to clarify to what extent PRS may facilitate individualized PD risk prediction for mutation carriers of monogenic PD.
In the final objective (Objective 5), we will combine MR and PRS. We will use the developed PRS for PD as instrumental variables for MR and investigate the causality of PD for several outcomes such as behavioral traits.
The PIs of P8 have extensive expertise in the field of statistical methods for genetic epidemiology. The objectives of P8 will be pursued in close collaboration with P1, P2, P4, P5, P9 and P10 and Core Facility Genetic Replication and Validation in Z2.
Physiological relevance of genetic risk variants in reduced penetrance in movement disorders
To date, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified thousands of loci associated with hundreds of complex diseases and traits. In more recent years, considerable progress has been made in elucidating the causal variants and genes underlying these associations. However, functional characterization of the mechanisms in GWAS loci is a complex challenge. These challenges include linkage disequilibrium and allelic heterogeneity at each locus, the non-coding nature of most loci, and the time and cost required to evaluate the potential mechanistic contributions of genes and variants experimentally. Furthermore, any signal within a locus can affect the same or different target genes. Identifying mechanisms responsible for GWAS loci requires an accumulation of consistent evidence for the genes and variants that influence the trait or disease in humans. Experimental studies on genes and variants may differ based on cell type, cell environment, or other context-specific variables. In P9 we will make use of established in silico as well as in vitro workflows to elucidate the physiological relevance of genetic variants in reduced penetrance of Parkinson’s disease (PD), dystonia, and X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (XDP). As a starting point, we will use multiple candidate regions identified on nine chromosomes through the GWAS approach in the first funding period of ProtectMove (projects P5-P7). These will further be analyzed in a systematic, comprehensive, and organized fashion with the goal to create an efficient and standardized workflow that would provide an informative overview of findings and allow for recognition of ensuing patterns, and their overall relevance for reduced penetrance in hereditary movement disorders. Briefly, in Objective 1 we will perform in silico evaluation and prioritization of variants/regions identified in the GWASs mentioned above. In Objective 2 we will employ a variety of experimental strategies to elucidate the mechanisms and physiological relevance of the most compelling (and currently for the most part unknown), variants from Objective 1. Finally, in our Objective 3, we will modulate elements regulating the genes with disturbed (down or up-regulated) expression to compensate for the detected dosage effects. Thus, we aim not only to identify and functionally characterize the variants modifying penetrance and expressivity of PD, dystonia, and XDP, but also to devise means for boosting or ameliorating their effect.
Identifying Parkinson’s disease penetrance-modifying factors in the population-based Cooperative Health Research in South Tyrol (CHRIS) cohort
The largest described pedigree of Parkin mutation carriers (n=77) originates from South Tyrol and includes numerous heterozygous carriers of Parkin mutation carriers who develop overt symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (PD), while others may have prodromal, or no obvious symptoms. We aim to dissect out the factors that modify the penetrance of these variants, using additional mutation carriers in the Cooperative Health Research in South Tyrol (CHRIS) study (n=13,490 from the same geographical region). In the first funding period, testing whether factors that influence mitochondrial function can alter penetrance of nuclear mutations causing mitochondrial dysfunction, we observed an increased burden of mtDNA mutations in affected vs. unaffected heterozygous Parkin and PINK1 (Phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1) mutation carriers and compared to non-carriers, which might explain the phenotypic (clinical, sub-clinical) discordance in these individuals with similar nuclear genetic background. However, the specificity of mtDNA variation as a penetrance marker and the molecular pathways of increased mtDNA mutation load ultimately leading to neurodegeneration, require further investigation with larger datasets. We hypothesize that there will be a penetrance-modifying interaction between mutations in PD genes and mitochondrial function, influenced by both mtDNA mutation burden and/or copy number, through mechanisms that involve mtDNA maintenance. In Objective 1, we will identify additional Parkin mutation carriers (expected total n=650) in the CHRIS study and characterize them phenotypically for signs and symptoms of prodromal or overt PD. From a successful recall-by-genotype pilot study, we have established the ethics framework to recall carriers for deeper phenotyping and identified phenotypes that appear able to distinguish carriers and non-carriers in the pilot study. Using deep mitochondrial sequencing, in Objective 2, we will determine the mtDNA mutational load and damaging mtDNA variants in blood from carriers of pathogenic Parkin variants identified in Objective 1. We will test whether these variables influence disease penetrance/expressivity, and specifically look whether it is possible to detect a threshold of mutation burden that predicts sub-clinical or clinical phenotype appearance. In Objective 3, we will test the causal link between pathogenic variants in Parkin, mtDNA mutations and expressivity of molecular phenotypes of mitochondrial function in neuronal cell models, and test mechanisms that might rescue mitochondrial function in the presence of such Parkin and mtDNA variants. We will characterize biosamples drawn from participants at different time points to see changes over time. This might allow interventional studies to test neuroprotective strategies (genetic or pharmacological) aimed at normalizing mitochondrial function in the presence of Parkin mutations, or in other genes that influence mitochondrial function.

